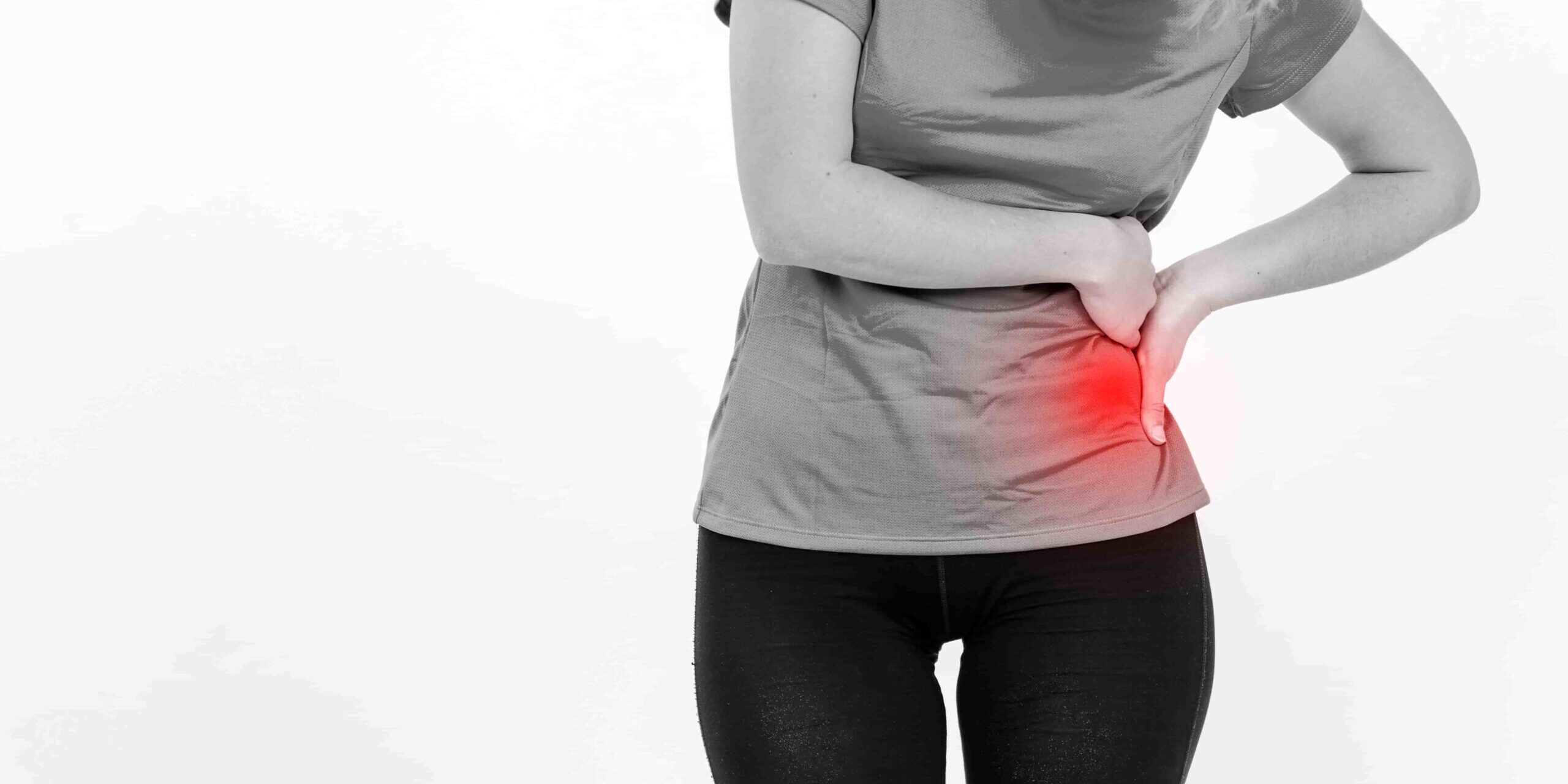
Pelvic pain refers to the pain in the lower region, in the area of your pelvic bone or reproductive organs. It is often felt in the lower part of your tummy, typically below the belly button. Pelvic pain can vary and it may be acute or sudden and severe (acute pelvic pain).
Chronic pelvic pain happens when the pain lasts 6 months or longer which impacts a person’s daily life and overall well-being. Understanding its symptoms can help your doctor discover the causes of chronic pelvic pain.
Understanding Chronic Pelvic Pain
Chronic pelvic pain is known as a complex condition that could be caused by various conditions, making it a little more challenging to diagnose and treat. Chronic pelvic pain can also happen to both men and women.
Understanding chronic pelvic pain syndrome is important to manage symptoms and treat the condition as there are a variety of underlying causes each with its own symptoms. Read on to dive deeper into chronic pelvic pain, the symptoms, causes and treatment.

Common Symptoms of Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Below is a list of common symptoms of chronic pelvic pain:
- A sharp and stabbing pain that happens suddenly.
- Pain that comes and goes.
- Dull aching or feeling of pressure.
- A cramping or throbbing pain.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Pain while urinating or having a bowel movement.
- Severe cramping before and during menstruation.
Causes of Chronic Pelvic Pain
There are many reasons why people may have chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The causes are quite diverse and can involve different systems within the body. For effective treatment, diagnosing the real cause of chronic pelvic pain is important. The causes of chronic pelvic pain in men and women are as below:
1. Gynaecological Conditions
For women having chronic pelvic pain, gynaecological conditions are one of the causes of the pain.
Endometriosis
This happens when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, which causes pain and inflammation.
Adenomyosis
In this case, the endometrial tissue grows into the muscle wall of the uterus which causes pain and heavy bleeding.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
An infection of the female reproductive organs that can lead to chronic pelvic pain.
Ovarian Cysts
Fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries that can cause pain as well as discomfort.
2. Urological Issues
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Recurrent or chronic infections in the urinary system.
Interstitial Cystitis
Also known as painful bladder syndrome, it’s typically linked within the bladder that keeps coming back and frequently needs to urinate. Pelvic pain happens when your bladder fills up.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Certain gastrointestinal disorders are also known to cause chronic pelvic pain.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
This is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine which causes cramping, abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits. Common symptoms of IBS are bloating, constipation and diarrhea.
Constipation or Diarrhea
These gastrointestinal issues can also lead to pelvic pain.
4. Musculoskeletal Problems
Health issues in the muscles and bones can also cause chronic pelvic pain. This includes:
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
This happens when the muscles in the pelvic floor don’t work properly, causing pain and discomfort.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Chronic pain in the muscles and fascia of the pelvic area, usually caused by muscle strain or injury.
5. Psychological Factors
For some people, the root of chronic pelvic pain is psychological, contributing to both the perception and intensity of pain.
Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress like anxiety can aggravate physical pain and contribute to the chronicity of symptoms.
Depression
Often associated with depression, this can further increase the intensity of the pain.
Diagnosing Chronic Pelvic Pain
To diagnose what is causing your pelvic pain, your doctor will ask you some questions regarding your symptoms. Your healthcare team may also ask you to keep a pain journal to keep a record of your pain experience as well as other symptoms that come along.
Diagnosing chronic pelvic pain, however, requires a thorough medical evaluation. You may need to do the tests below:
1. Lab Tests
You may need to do a blood test to measure your blood cell count or a urine test to check if there is a urinary tract infection.
2. Pelvic Exam
A comprehensive physical exam like a pelvic exam is done to find symptoms of any illnesses, unusual growths, or tense pelvic floor muscles. Do speak up if you encounter any pain during the pelvic exam.
3. Ultrasound
An ultrasound may also be carried out where sound waves are used to see the structures of organs and other parts inside the body. This also can help guide diagnosis and treatment for chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
4. CT or MRI Scans
A CT scan or MRI scan may be done to help find growths in the body such as cysts in the ovaries, fallopian tube or uterus.
5. Laparoscopy
This test is a small surgery done whereby a small cut is made in the stomach area and a small tube with a camera is placed through the cut. This allows the surgeon to check for any unusual tissues or infections through the camera.

Treatment Options for Chronic Pelvic Pain
Below are some of the treatment options available for Chronic Pelvic Pain:
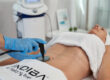
1. INDIBA Treatment
INDIBA treatment uses radiofrequency technology to treat chronic pelvic pain of inflammatory origin. The INDIBA 448 kHz radiofrequency device is used together with manual therapy to improve blood flow, reduce inflammation and promote fast tissue healing.
Clinical studies have shown that many patients experience a significant reduction in pain levels after just 10 physical sessions. This makes INDIBA an effective option for those suffering from chronic pelvic pain. According to clinical studies, the device is also known to be very safe for use.
2. Medications
Based on the underlying cause of pain, some medications are also often prescribed which include:
Pain Relievers: Certain pain relievers that can be bought over the counter without a prescription can be used to ease the pain. Such pain relievers are ibuprofen and aspirin. These medicines however only help to manage the pain.
Hormonal Treatment: For pain associated with gynaecological issues such as adenomyosis and endometriosis, hormonal treatments like birth control pills may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce pelvic pain that comes along with it.
Antibiotic: Antibiotics may be prescribed if an illness caused by bacteria is the source of your pelvic pain.
Antidepressants: Some antidepressants are also used in treating chronic pelvic pain even if you don’t have depression.
3. Physical Therapy
Other treatments such as physical therapy can also be highly effective in treating chronic pelvic pain. Certain exercises can be done to strengthen or relax the pelvic floor muscles to reduce the pain. Manual therapy includes techniques like soft tissue massage may also help to manage the pain.
4. Psychological Counseling
Some people suffering from chronic pelvic pain syndrome may be linked to psychological behaviour like depression or anxiety. Others may be caused by past traumas such as sexual or emotional abuse. Talking to a psychologist may help both the body and mind by addressing any underlying mental health issues that may exacerbate the pain.
5. Surgical Interventions
When other treatments are not working or an underlying condition is identified such as fibroids or endometriosis, surgical interventions are then being considered. These procedures include:
Laparoscopy: This is a minimally invasive surgery to remove any cysts present, endometrial tissue or adhesions.
Hysterectomy: In times like a severe or rare case, the removal of the uterus may be recommended if the other treatments are ineffective or if the pain is caused by certain conditions such as adenomyosis. You may also need to have one or both of your ovaries removed.
6. Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Lifestyle changes such as incorporating exercise or a dietary change can make a significant difference in managing chronic pelvic pain. Low-impact exercises such as walking, yoga, or even swimming can help reduce the pain. Eating anti-inflammatory foods can also help in alleviating the pain.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol that can trigger any symptoms of chronic pelvic pain. Other than that, stress management also plays an important role in managing chronic pelvic pain. Meditation, mindfulness and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety and thus, control the pain.
Ready to Treat Your Chronic Pelvic Pain?
Chronic pelvic pain is not to be taken lightly and it requires a comprehensive treatment approach. This often involves a combination of therapies. INDIBA offers an effective treatment along with other lifestyle interventions for managing this challenging and painful condition.
Our safe and effective radiofrequency technology is one of the effective ways to control chronic pelvic pain. If you are struggling with chronic pelvic pain, talk to your healthcare provider to explore your treatment options.